Click here for Installation of phpMyAdmin Tutorials
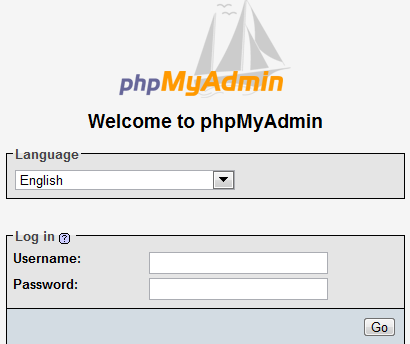
You can access your MySQL account using phpMyAdmin using the link provided to you --something like below
http://localhost/phpmyadmin
When you click on the link above, a
dialog box will prompt you for a username and password. This will be
the
username and password given you when we set it up for you.
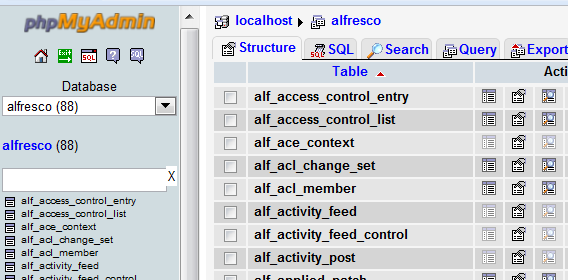
Once you log in, a phpMyAdmin screen appears as shown below.

Creating a table in your database
The left-hand
frame in phpMyAdmin is used for navigation.You will see your
database displayed here (in this case called mydomain). As you create
tables, they will show below this.
Click on your
database the navigation frame and a new window will
appear on the
right hand side.
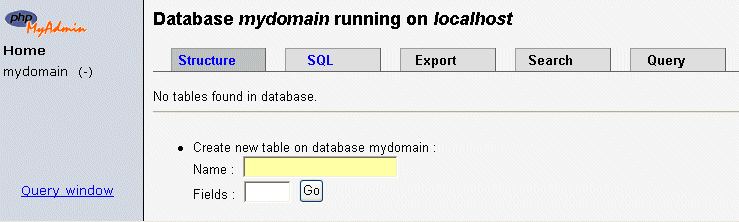
We will create a table in the database, called "people". Use the Create
new table feature. Type in the name of the
new table
into the Name: people, and the number of columns in the table
(4) into Fields:.
This tutorial is only designed to show you the basic
php/MySQL/phpMyAdmin functions.
You can delete it using the Drop function. You will
want to allow for growth in your table.
Click Go and you should see something like this.
The table title now appears with under the database name.

Now enter the names and attributes of our table fields. Enter the
following
information as above:
| Field | Type | Length | Default |
Extra |
| id | int | 6 | 0 |
auto_increment |
| name | char | 100 | ||
| telephone | char | 50 | ||
| birthday | char | 50 |
The Length value indicates the maximum allowable length of
characters for input. There are many different
values that can be set for Type; see
further documentation here. The Types specified in this example
aren't the
most efficient, but just used for the purposes of this exercise. The
"id" field, which will be used as a Primary key for this table,
has been set to auto_increment, saving you from having to
having to type in the next number in
sequence when you input records. Set the Default to 0
Once you've
entered all the values, click Save. A screen like this
will appear.
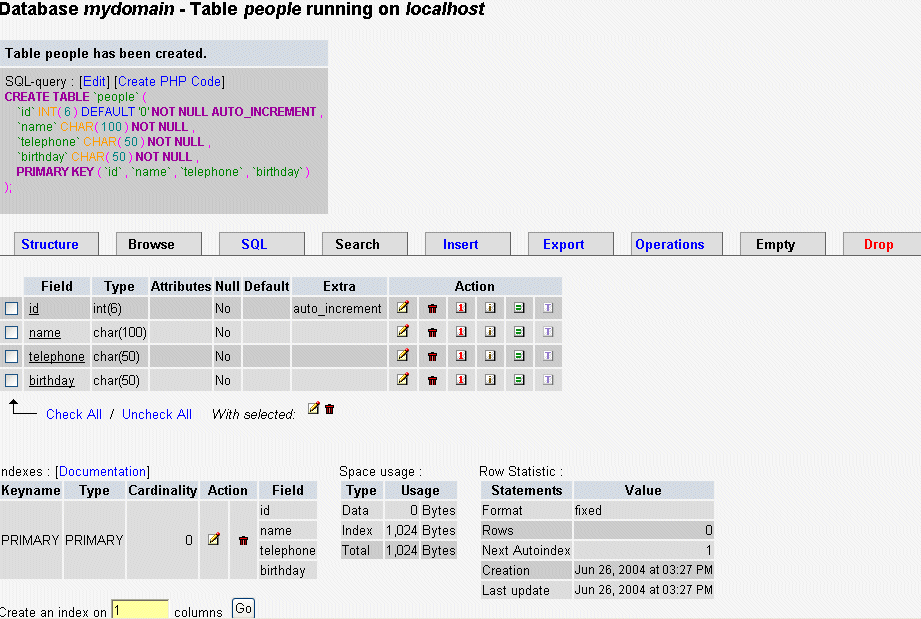
Congratulations!-You have created your table! The corresponding SQL
command for
creating these fields is also displayed. This isn't needed but in time
you will start to recognise MySql commands
Note that you can use Drop to delete a table or fields.
Note that you can use Drop to delete a table or fields.
When you are ready we suggest you check out all of the options
on this page.
Inputting data
into the table.
Click the
tab labeled "Insert" - and another window should appear, like
this.
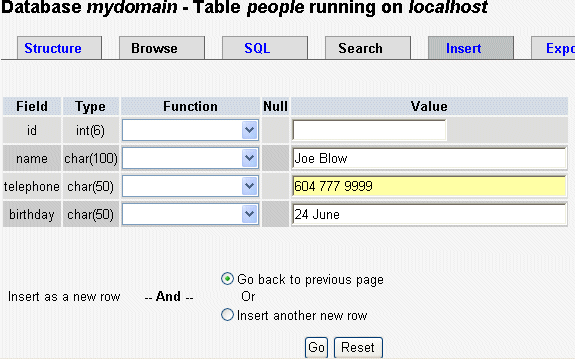
Now type in the details for each of the fields for this record. The
"id" column was set to automatically increment so you do not need
to enter a number.
Note - if you ever get lost with
phpMyAdmin
navigation click "Home" in the left hand nav bar and start
again.
Now click Save and the record is saved to the people table.
The previous window reappears with the SQL command for the insert. You can keep adding recordsby re-selecting Insert".
For multiple records, you can select the "Insert another new row" radio button on the input form.
The previous window reappears with the SQL command for the insert. You can keep adding recordsby re-selecting Insert".
For multiple records, you can select the "Insert another new row" radio button on the input form.
When you've finished entering several records into the table,
you can check them
by
clicking on the Browse tab. You can click on individual
records for editing or
deleting.
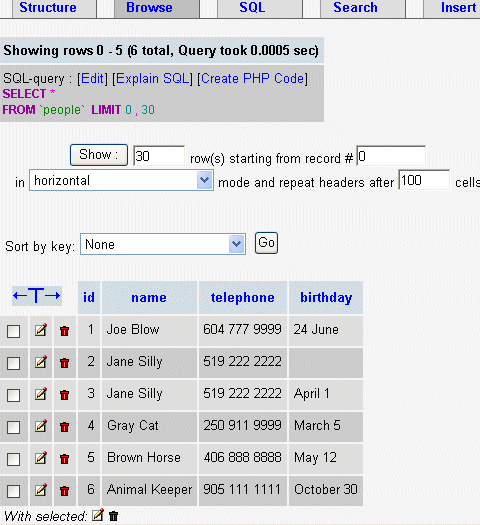
You can use the Select tab to refine your display when your database
starts grows to many pages
of records.
Backup your
data
You "don't know what you've got 'til its gone"!
- Click on your
database name in the left hand navigation bar
- Click on EXPORT (top tab)
- Highlight the table/s you want to back up
- Select STRUCTURE and DATA radio button
- Highlight the table/s you want to back up
- Select STRUCTURE and DATA radio button
- Select "Enclose table and field names with backquotes"
- Select "Save as file" and "zipped" check boxes
- Click "Go" and a zipped archive file will be generated.
- Select "Save as file" and "zipped" check boxes
- Click "Go" and a zipped archive file will be generated.
Well done! -
you've created a database, a table and fields, entered in a few
records, viewed the
records, edited and perhaps deleted some of them and practised
backing up.